Abstract
Letter to Editor
Serum MicroRNA-155 in Acute Graft-Versus-Host-Disease (aGVHD)
Yvonne A Efebera*, Amy S Ruppert, Apollinaire Ngankeu, Sabrina Garman, Prasanthi Kumchala, Alan Howard, Steven M Devine, Parvathi Ranganathan and Ramiro Garzon
Published: 16 August, 2019 | Volume 2 - Issue 1 | Pages: 079-082
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHSCT) is a curative treatment for many hematologic malignancies. Unfortunately, about 30-50% of all recipients undergoing alloHSCT develop acute graft-versus-host-disease (aGVHD), which is associated with high morbidity and mortality [1,2]. Treatment of aGVHD involves the use of immune suppressive drugs such as high dose of steroids that leads to further immunosuppression and risk for opportunistic infections. Often patients are refractory to steroids therapy making the prognosis dismal. Thus, it is critical to identify robust biomarkers to detect aGVHD before onset of clinical symptoms so that therapeutic strategies can be implemented that may result in better treatment responses and less toxicity.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001007 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Mir-155; Graft versus host disease, MicroRNA; Allogeneic stem cell transplant
References
- Blazar BR, Murphy WJ, Abedi M. Advances in graft-versus-host disease biology and therapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012; 12: 443-458 PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22576252
- Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E. Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 2009; 373: 1550-1561. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19282026
- Paczesny S. Discovery and validation of graft-versus-host disease biomarkers. Blood. 2013; 121: 585-594. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23165480
- Paczesny S, Braun TM, Levine JE, Hogan J, Crawford J, et al. Elafin is a biomarker of graft-versus-host disease of the skin. Sci Transl Med. 2010; 2: 13ra2. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20371463
- Paczesny S, Krijanovski OI, Braun TM, Choi SW, Clouthier SG, et al. A biomarker panel for acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2009; 113: 273-278. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18832652
- Reichenbach DK, Schwarze V, Matta BM, Tkachev V, Lieberknecht E, et al. The IL-33/ST2 axis augments effector T-cell responses during acute GVHD. Blood. 2015; 125: 3183-3192. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25814531
- Vander Lugt MT, Braun TM, Hanash S, Ritz J, Ho VT, et al. ST2 as a marker for risk of therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease and death. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369: 529-539. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23924003
- Ali AM, DiPersio JF, Schroeder MA. The Role of Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Risk Stratification of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Systematic Review. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22: 1552-1564. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27158050
- Paczesny S, Levine JE, Braun TM, Ferrara JL. Plasma biomarkers in graft-versus-host disease: a new era? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009; 15: 33-38. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19147075
- Xiao B, Wang Y, Li W, Baker M, Guo J, et al. Plasma microRNA signature as a noninvasive biomarker for acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2013; 122: 3365-3375. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24041574
- Wang Y, Zhao X, Ye X, Luo H, Zhao T, et al. Plasma microRNA-586 is a new biomarker for acute graft-versus-host disease. Ann Hematol. 2015; 94: 1505-1514. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26051902
- Xie LN, Zhou F, Liu XM, Fang Y, Yu Z, et al. Serum microRNA155 is increased in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease. Clin Transplant. 2014; 28: 314-323. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24494749
- Atarod S, Ahmed MM, Lendrem C, Pearce KF, Cope W, et al. miR-146a and miR-155 Expression Levels in Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease Incidence. Front Immunol. 2016; 7: 56. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27014257
- Chen S, Smith BA, Iype J, Prestipino A, Pfeifer D, et al. MicroRNA-155-deficient dendritic cells cause less severe GVHD through reduced migration and defective inflammasome activation. Blood. 2015; 126: 103-112. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25972159
- Ranganathan P, Heaphy CE, Costinean S, Stauffer N, Na C, et al. Regulation of acute graft-versus-host disease by microRNA-155. Blood. 2012; 119: 4786-4797. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22408260
- Wingard JR, Carter SL, Walsh TJ, Kurtzberg J, Small TN, et al. Randomized, double-blind trial of fluconazole versus voriconazole for prevention of invasive fungal infection after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2010; 116: 5111-5118. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20826719
Figures:
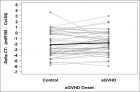
Figure 1
Similar Articles
-
Impact of Intravenous Busulfan Pharmacokinetics on Safety in Pediatric Patients who have undergone Hematopoietic Stem Cell TransplantOmar AL Mofleh*,Noha Awadalla,Amal AL Shafi,Lina Husain,Hanan AL Musabeh,Saad AL Daama. Impact of Intravenous Busulfan Pharmacokinetics on Safety in Pediatric Patients who have undergone Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001018; 7: 007-012
Recently Viewed
-
Febrile Lumbar Pain Revealing a Massive Collection: Complicated Psoas Abscess Managed SurgicallyMohammed Amine Elafari*,Mamad Ayoub,Mohammed Amine Bibat,Rhayour Anas,Maachi Youssef,Amine Slaoui,Tarik Karmouni,Abdelatif Koutani,Khalid Elkhader. Febrile Lumbar Pain Revealing a Massive Collection: Complicated Psoas Abscess Managed Surgically. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001041; 10: 010-012
-
Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A ReviewNeeraj Kumar*,Dev Brat Mishra. Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A Review. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001036; 9: 015-019
-
Phenotypic differences in Obese Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) - A Mini ReviewMichelle Nanni*, Vivian Hu, Swagata Patnaik, Alejandro Folch Sandoval, Johanna Contreras. Phenotypic differences in Obese Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) - A Mini Review. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001020; 8: 001-005
-
Stone on the Mesh: Intravesical Erosion after Laparoscopic Promontofixation-A Hidden Cost of DurabilityAyoub Mamad*,Mohammed Amine Bibat,Mohammed Amine Elafari,Midaoui Moncef,Amine Slaoui,Tarik Karmouni,Abdelatif Koutani,Khalid Elkhader. Stone on the Mesh: Intravesical Erosion after Laparoscopic Promontofixation-A Hidden Cost of Durability. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001040; 10: 006-009
-
Feasibility study on the evaluation of the effect of narrow-band CE-Chirp ASSR in the hearing field after hearing aid in hearing-impaired childrenWang Yonghua*,Xing Shuoyao. Feasibility study on the evaluation of the effect of narrow-band CE-Chirp ASSR in the hearing field after hearing aid in hearing-impaired children. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001007; 3: 007-011
Most Viewed
-
Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Preeyapat Chattieng,Tiersidh Nasomphan,Korbtham Sathirakul. Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001026; 7: 00-007
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
-
Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging PresentationKarthik Baburaj*, Priya Thottiyil Nair, Abeed Hussain, Vimal MV. Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging Presentation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001029; 8: 001-003
-
Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-goDaniel Gandia,Cecilia Suárez*. Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-go. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001033; 7: 001-002
-
The benefits of biochemical bone markersSek Aksaranugraha*. The benefits of biochemical bone markers. Int J Bone Marrow Res. 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001013; 3: 027-031

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."