Figure 6
Novel European Asiatic Clinical, Laboratory, Molecular and Pathobiological (2015-2020 CLMP) criteria for JAK2V617F trilinear polycythemia vera (PV), JAK2exon12 PV and JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL515 thrombocythemias: From Dameshek to Constantinescu-Vainchenker, Kralovics and Michiels
Jan Jacques Michiels*, King H Lam, Fibo Ten Kate, Dong-Wook Kim, Myungshin Kim, Vasily Shuvaev, Francisca Valster, Vincent Potters, Wilfried Schroyens, Mihaela Andreescu, Adrian Trifa, Achille Pich and Hendrik De Raeve
Published: 03 April, 2020 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-020
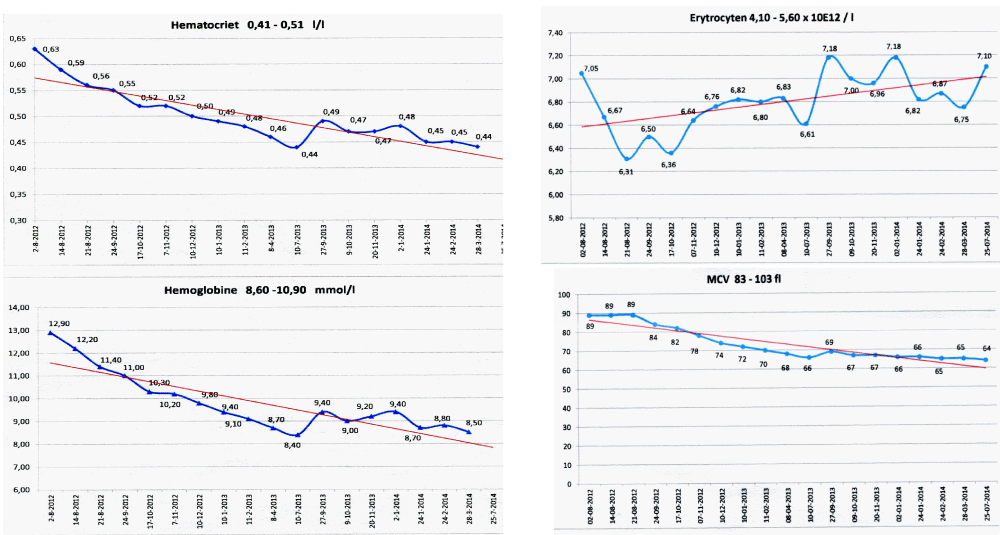
Figure 6:
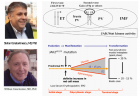
State of the art treatment according to Dameshek [2,4] of a newly diagnosed PV patient (Ht 0.63, Hb 12.9 mmol/L, erythrocytes 7.1 x1012/L and MCV 89 fL) with repeated vene sections as confirmed by Pearson & Wetherley-Mein [48] and Messinazy, et al. [49] of the London PV Study Group [46,47]. Repeated venesections for more than 1 year (from August 2012 to September 2013) was needed to induce a complete hematological remission (CHR) reaching the desired plateau of Ht 0.45, Hb 9.0 mmol/L, and MCV of 66 fL. While on low dose aspirin neither microvascular nor major thrombosis did occur. Once the iron deficiency state is reached the erythrocytes remain microcytic and reach values of 7.0 to 7.2x1012/L without further need of phlebotomy due to the persistence of the iron deficienct state [2,30]. Correction of the Ht from 0.63 to below 0.45 is associated with reduction of major venous and arterial thrombotic events [8,9,48,51], but the microvascular thrombotic syndrome of associated thrombocythemia persisted. Low dose aspirin in ET in the Dutch Collaborative Low dose Aspirin in Thrombocythemia (Dutch CLAT) Van Genderen studies [89-91,99] and low dose aspirin on top of phlebotomy or hydroxurea in the European Collaborative Low dose Aspirin in PV (ECLAP, [50]) reduced the incidences of microvascular disturbances and major thrombosis from above 50% per 100 pt/yr to less than 3% per 100 pt/yr in both ET and PV [91,94], but does not prevent the progression of JAK2 mutated MPN disease in terms of JAK2 mutation load, MPN disease burden like progressive leukocythemia, thrombocythemia, splenomegaly and constitutional symptoms [6,7,34].
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001011 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
More Images
Similar Articles
-
European Clinical Laboratory, Molecular and Pathological (ECMP) criteria for prefibrotic JAK2V617F-Thrombocythemia and Polycythemia Vera versus MPL515- and CALR-Thrombocythemia and Myelofibrosis: From Dameshek to Michiels 1950-2018Jan Jacques Michiels*,Zwi Berneman,Wilfried Schroyens,Fibo W J ten Kate,King Lam,Hendrik De Raeve. European Clinical Laboratory, Molecular and Pathological (ECMP) criteria for prefibrotic JAK2V617F-Thrombocythemia and Polycythemia Vera versus MPL515- and CALR-Thrombocythemia and Myelofibrosis: From Dameshek to Michiels 1950-2018. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001002; 2: 001-017
-
Primary myelofibrosis is not primary anymore since the discovery of MPL515 and CALR mutations as driver causes of mono-linear megakaryocytic and dual megakaryocytic granulocytic myeloproliferation and secondary myelofibrosisJan Jacques Michiels*,Hendrik De Raeve. Primary myelofibrosis is not primary anymore since the discovery of MPL515 and CALR mutations as driver causes of mono-linear megakaryocytic and dual megakaryocytic granulocytic myeloproliferation and secondary myelofibrosis. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001003; 2: 018-026
-
The PVSG/WHO versus the Rotterdam European clinical, molecular and pathological diagnostic criteria for the classification of myeloproliferative disorders and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPD/MPN): From Dameshek to Georgii, Vainchenker and Michiels 1950-2018Jan Jacques Michiels*,Hendrik De Raeve. The PVSG/WHO versus the Rotterdam European clinical, molecular and pathological diagnostic criteria for the classification of myeloproliferative disorders and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPD/MPN): From Dameshek to Georgii, Vainchenker and Michiels 1950-2018. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001004; 2: 027-050
-
Bone marrow histology in CALR mutated thrombocythemia and myelofibrosis: Results from two cross sectional studies in 70 newly diagnosed JAK2/MPL wild type thrombocythemia patientsJan Jacques Michiels*,Yonggoo Kim,Myungshin Kim,Francisca Valster,Vincent Potters,Zwi Berneman,Alain Gadisseur,Wilfried Schroyens,Hendrik De Raeve. Bone marrow histology in CALR mutated thrombocythemia and myelofibrosis: Results from two cross sectional studies in 70 newly diagnosed JAK2/MPL wild type thrombocythemia patients. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001006; 2: 064-078
-
Novel European Asiatic Clinical, Laboratory, Molecular and Pathobiological (2015-2020 CLMP) criteria for JAK2V617F trilinear polycythemia vera (PV), JAK2exon12 PV and JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL515 thrombocythemias: From Dameshek to Constantinescu-Vainchenker, Kralovics and MichielsJan Jacques Michiels*,King H Lam,Fibo Ten Kate,Dong-Wook Kim,Myungshin Kim,Vasily Shuvaev,Francisca Valster,Vincent Potters,Wilfried Schroyens,Mihaela Andreescu,Adrian Trifa,Achille Pich,Hendrik De Raeve. Novel European Asiatic Clinical, Laboratory, Molecular and Pathobiological (2015-2020 CLMP) criteria for JAK2V617F trilinear polycythemia vera (PV), JAK2exon12 PV and JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL515 thrombocythemias: From Dameshek to Constantinescu-Vainchenker, Kralovics and Michiels. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001011; 3: 001-020
Recently Viewed
-
Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices of Parents toward (Infant & Child) Oral Health in Family Medicine Center at PSMMC, RiyadhMaryam Alanazi*, Wed Alanazi, Hanan Alali, Fatma Alnoaimi, Arwa Shuwaykan, Nuha Al-Yahya. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices of Parents toward (Infant & Child) Oral Health in Family Medicine Center at PSMMC, Riyadh. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001044; 8: 016-023
-
Success, Survival and Prognostic Factors in Implant Prosthesis: Experimental StudyEpifania Ettore*, Pietrantonio Maria, Christian Nunziata, Ausiello Pietro. Success, Survival and Prognostic Factors in Implant Prosthesis: Experimental Study. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001045; 8: 024-028
-
A Resurgence of the Idea of Hypertriglyceridemia and Lower Serum (HDL-C) as Predictive Factors for Insulin Resistance (IR) & Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Development: A Narrative ReviewKulvinder Kochar Kaur*. A Resurgence of the Idea of Hypertriglyceridemia and Lower Serum (HDL-C) as Predictive Factors for Insulin Resistance (IR) & Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Development: A Narrative Review. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001022; 9: 001-012
-
Novel Mutation in Famous Gene Diseases in Red Blood CellsMahdi Nowroozi*. Novel Mutation in Famous Gene Diseases in Red Blood Cells. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001023; 9: 013-020
-
Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical TrialAnders Wänman*, Susanna Marklund, Negin Yekkalam. Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001046; 9: 001-008
Most Viewed
-
Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Preeyapat Chattieng,Tiersidh Nasomphan,Korbtham Sathirakul. Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001026; 7: 00-007
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
-
Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging PresentationKarthik Baburaj*, Priya Thottiyil Nair, Abeed Hussain, Vimal MV. Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging Presentation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001029; 8: 001-003
-
Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-goDaniel Gandia,Cecilia Suárez*. Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-go. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001033; 7: 001-002
-
The benefits of biochemical bone markersSek Aksaranugraha*. The benefits of biochemical bone markers. Int J Bone Marrow Res. 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001013; 3: 027-031

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."